Apache HBase has long been the database of choice for business-critical applications across industries. This is primarily because HBase provides unmatched scale, performance, and fault-tolerance that few other databases can come close to. Think petabytes of data spread across trillions of rows, ready for consumption in real-time. While application developers and database admins are well aware of the benefits of using HBase, they also know about a few shortcomings that the database has historically had. These shortcomings come in the form of the time it takes to deploy a new instance, and getting the sizing, management, and performance optimizations right. Additionally, a big share of HBase applications are deployed on premises and there’s been an ever-growing need for an easy way to move these applications to the public or hybrid cloud while maintaining enterprise-grade security and governance.
In this blog, we’ll talk about Cloudera Operational Database (COD), a DBPaaS offering available on Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) that brings all the benefits of HBase without any of the overheads. COD offers a clear pathway for developers and admins that are looking for a friction-free way to migrate existing HBase applications to the public cloud. Here are the top five reasons why COD is an obvious choice:
Built for the cloud
Cloudera has had HBase as part of its legacy offerings (CDH and HDP) on premises for many years. Looking at how hundreds of customers were using it, we realized that many were already deploying HBase in the public cloud in an IaaS form factor. This meant that although applications were deployed on a public cloud, developers were not able to tap into some of the benefits that cloud-native services offer and were still having to deal with HBase deployment and management overheads.
COD on Cloudera Data Platform provides a far superior way than IaaS when it comes to deploying HBase in the public cloud. It’s a cloud-native data service that is available on AWS, Azure, and GCP. It provides auto-scalability that ensures cloud consumption is always in line with performance and application requirements. And as a turn-key, DBPaaS offering, it also ensures that there’s no setup, sizing, or performance tuning required when deploying an instance.
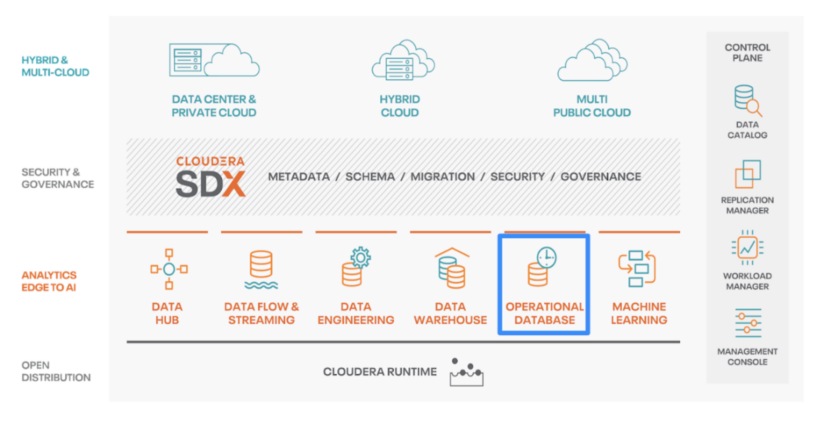
COD in the Cloudera Data Platform (CDP)
Flexible and multi-modal
There are two things to note here when considering flexibility. First, COD provides both NoSQL and SQL approaches to querying data. For developers who prefer SQL, COD comes with Apache Phoenix, which provides familiarity of access with support for ANSI SQL. Developers can choose three different modes of operation: key-value, wide-column, or relational wide-column using either our No-SQL client (Java APIs) or JDBC/ODBC.

Second, there is also flexibility in terms of schema. COD supports evolutionary schema, which allows changes to data models without having to re-architect applications. COD enables enterprises to bring together and process more data of different types that can be used for a broad range of applications ranging from serving machine learning models to mobile applications.
Security, governance, and control
As COD is a part of CDP, security is built in. SDX, or Shared Data Experience, on CDP enables users to easily create, manage, and maintain multi-tenant data access policies through standardization and seamless enforcement of granular, dynamic role- and attribute-based security rules. This eliminates business and security risks and ensures compliance by preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. In addition, all data is always stored in the customer’s cloud account. Control plane on CDP provides Replication Manager which enables you to replicate, export, and take snapshots of data manually or as scheduled automated tasks. Replication manager also enables admins to enable disaster recovery as a use case.
High availability (multi-AZ)
A multi-AZ deployment means that compute infrastructure for HBase’s master and region servers are distributed across multiple availability zones ensuring that when a single availability zone has an outage, only a portion of region servers will be impacted and clients will automatically switch over to the remaining servers in the available AZs. This ensures that the database won’t be impacted in case the cloud provider has an outage for one of the availability zones. You can learn more about multi-AZ in this in-depth blog we published recently.
Field tested
We launched COD a little more than a year ago. Since its launch many customers who were looking for a way to move applications to the public cloud have adopted it. If you would like to know more then here’s the story of one of our customers that is saving $1.5 million annually with COD. But even before the product’s general availability we worked closely with customers to learn what HBase as a DBPaaS should look like. We worked closely with these customers to understand migration and production workloads so when the product is available for everyone it will deliver on its promise.
In addition to the five reasons highlighted above COD is also incredibly easy to use. A streamlined UI and autonomous features ensure a click-and-forget experience. Don’t believe us? We’ve created a walk-through demo for you to experience COD on your own. If you would like to know more, join us for a webinar on the topic of developing and deploying enterprise applications with Cloudera Operational Database on September 7, 2022.



